Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy is a serious eye condition resulting from diabetes mellitus, which can lead to damage to the retinal blood vessels in the back of the eye. Left untreated, it can even result in permanent blindness. Here, we’ll delve into the causes, types, and methods of diagnosing diabetic retinopathy, emphasizing the importance of early detection and proper treatment.
Causes of Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy primarily stems from the effects of high blood sugar levels on the delicate blood vessels within the retina, the nerve layer responsible for sensing light and transmitting visual information to the brain.
The Two Stages of Diabetic Retinopathy
Non-Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (NPDR)
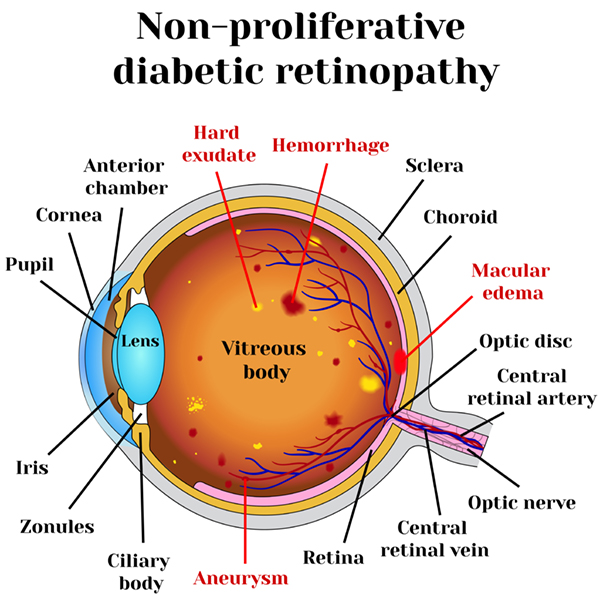
NPDR, also known as background retinopathy, represents the early stages of diabetic retinopathy. In this phase, tiny blood vessels within the retina may leak blood or fluid, causing the retina to swell or develop deposits known as exudates.
Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (PDR)
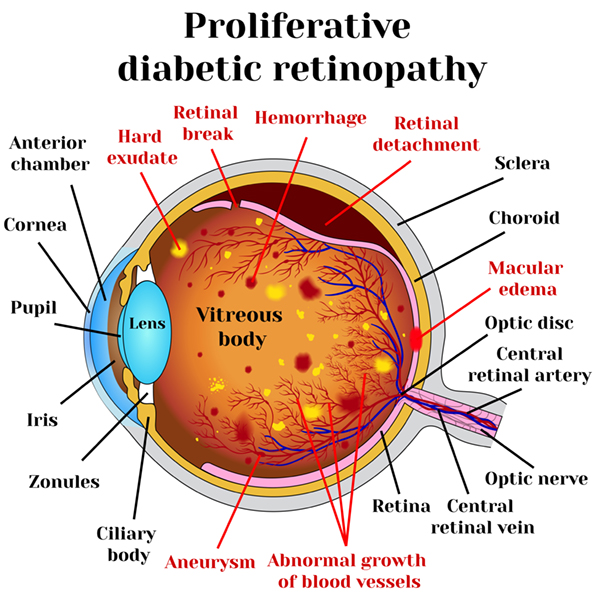
PDR is the advanced stage, characterized by the growth of abnormal new blood vessels on the retina’s surface or optic nerve. The main cause of PDR is widespread closure of retinal blood vessels, leading to inadequate blood flow. In response, the retina generates new blood vessels in an attempt to compensate. Unfortunately, these abnormal vessels do not restore normal blood flow and may be accompanied by scar tissue, which can lead to retinal wrinkling or detachment. PDR can result in more severe vision loss, affecting both central and peripheral vision.
Diagnosis of Diabetic Retinopathy
Early detection of diabetic retinopathy is crucial for effective treatment and vision preservation. Diagnosis methods include:
Dilated Eye Exam
A dilated eye examination allows your eye doctor to examine the retina for signs of diabetic retinopathy. It involves the use of special eye drops to dilate the pupils, providing a better view of the retina’s condition.
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)
This imaging technique is especially useful for detecting mild cases of diabetic retinopathy. It provides detailed cross-sectional images of the retina, allowing for a comprehensive assessment of its health.
Fluorescein Angiogram
For more severe cases, a fluorescein angiogram may be necessary. This diagnostic procedure involves injecting a fluorescent dye into a vein and capturing images as the dye circulates through the blood vessels in the retina. It helps assess the seriousness of the disorder.
Early Detection Saves Vision
As with many retinal conditions, early detection and timely treatment are pivotal for preserving vision in cases of diabetic retinopathy. If you experience symptoms or have diabetes mellitus, such as changes in vision, please do not hesitate to schedule an appointment with one of our retina specialists. Together, we can help manage and treat diabetic retinopathy effectively, providing you with the best possible care to safeguard your vision.
